This dissertation is based on experiences of parents whose children have been hospitalised for a very long time. It is quite stressful for parents to witness such an event and seeing their child in pain enhances feelings of despair, depression and pain. Parents witness a significant and high level of distress and in some cases, clinically harmful levels of post-traumatic symptoms. Long-term suffering of their child have a tedious and excruciating impact on the emotional facet of the parents as well. Such a high levels of nervousness and tension causes long-term, and sometimes permanent, exasperation. This kind of negative behaviour amplifies when the child is younger than 5 or 6 years. Hospitalisation of child induces negative changes in lives of parents and drastic shift in their daily routine. The key aspects in this dissertation are parents, hospitalisation, diseases, care home, medical treatment, child professionals, etc.
Definition of Key Terms
The dissertation is based on experiences of parents who have witnessed long term hospitalisation of their child. There are various key terms which are required to be defined. These terms are mentioned below:
- Parents:These individuals brings forth or begets offspring. They nurtures and raise their children and provide extensive and selfless care to them. It includes people who biologically reproduce children and those who are given responsibilities to parent a child. Â It could include foster and adoptive parents.
- Diseases:This refers to the condition which induces illness and abnormal and harmful physical symptoms within an individual's body. These have negative effects on a person's body and have vile characteristics which requires immediate medical attention.
- Hospitalisation:This term refers to a condition where individuals suffering form illness or disease gets admitted to a health care centre or hospital to receive adequate medical treatment for that illness.
- Medical Treatment:It means the care and management where medical professional tends patients to help them combat with a disorder, illness, disease. For parents whose children suffers from a disease or serious medical condition sometimes are reluctant to go beyond a certain level of medical treatment seeing risks and cost of the same.
- Care Home:These organisations or institutions are associated with providing effective care and fulfilment of needs of individuals who are either orphans or somehow have failed to acquire a shelter for themselves.
Incidence and prevalence / statistics
Hospitalisation of children adversely and negatively impact the parents' emotional and physical well-being. It is that sort of experience which induces fear and negative levels of anxiety within an individual. Recent studies reveal that the child hospital stays in England are rising. From past decade, the admission of infants have increased by more than 50% as compared to the last decade. There have also been substantial increase in the admission rate of children aged between one and four to about 25% (Child hospital stays 'keep rising', 2019). In addition to this, with hospitalisation of children, parents tend to be quite disturbed and distracted in finding balance between their routine and the issues associated with their child. Another analysis denote that almost 40% of parents experience high level of anxiety even after 3 months of discharge of their child (Parental anxiety and stress during children's hospitalisation, 2011). Substantial stress levels along with anger and pessimism are the impacts on parents experiencing hospitalisation of their offspring.
You Share Your Assignment Ideas
We write it for you!
Most Affordable Assignment Service
Any Subject, Any Format, Any Deadline
Order Now View Samples
Relevant Policies and Guidance
In recent times, there are various guidelines and policies set out for providing effective child care and support provided to them. With enhancements in awareness in recent times, the government of the UK is carving out more appropriate and systematic guidelines to ensure better health of children. In other words, the government and few organisations are taking initiatives which could contribute in betterment of children's health. For instance, the government of the UK is paying more attention towards pollution which could cause asthmatic and lung infections in children. Moreover, food production regulations by the government also indicates various guidelines which emphasize on quality production of food items provided to children without added preservatives or food colouring. Such guidance and effective policies would focus on preventing any sort of condition that could cause serious illness or diseases in children.
Summary of Existing Literature
As per the view points of Wray J., and et. al. (2019), parents tend to receive high level of stress during hospitalisation of their children. In addition, hospital service tend to influence as to how these parents cope with the condition of their child. Majority of parents experience anxiety at clinical levels and their condition remains the same even after months of discharge. They tend to be pessimistic and feel uncertainty regarding the illness. Such characteristics indicate worsening of physical and emotional condition of parents whose children are hospitalised. However, there are various interventions are made to increase coping of parents during the hospitalisation of their child.
More Suggested:Â
Rationale of the Research
The above reviewed literature brings out the experience of parents throughout and even after the time their children have been hospitalised. This research covers a very wide area of research where the emphasis would be completely on the experience of parents. Moreover, diseases will also be highlighted which causes such long-term hospitalisation. This research would be useful to gather initial warning and symptoms which require immediate medical attention to reduce the possibility of such long span of hospitalisation. It would also be helpful for individuals who seek to develop the professional criteria for learner in Health Care.
Development of Research Question
What are the experiences of parents/carers whose child has required long term hospitalisation?
Aims and Objectives
Research Aims
- To understand parents/carers experiences of their child's long term hospitalisation.
- To analyse the impact long term hospitalisation has on parents/carers.
Research Objectives
- To improve the experience of long term hospitalisation for parents/carers in future practice.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of current practice and support networks available to parents/carers whose child has experienced long term hospitalisation.
Chapter 2- Methodology
After brief introduction, the next step requires the researchers to identify and determine the methodologies used throughout the dissertation, its critical evaluation tool as well as method of analysis.
Search Strategy
Formulation of Key Terms
Each question has several key terms which are required to be identified for gaining a better understanding of the subject matter. It is imperative that the question is well focused for researcher to determine appropriate and effective resources as well as search for relevant and applicable evidence. For this specific issue, the framework that would serve quite appropriately for the research would be PICO framework. This term stands for: Population, Intervention, Comparison and Outcome. The framework is utilised to identify evidence-based practice resources. For the current research question. After identification of each key term, it is also imperative to find alternative terms for those words which are wild cards and truncations. While the former is used for alternate spellings, the latter is used for alternate endings.. The PICO framework is analysed below:
Research Question:Â What are the experiences of parents who have witnessed long term hospitalisation of their child?
|
POPULATION
|
Â
|
INTERVENTION
|
Â
|
OUTCOME
|
|
Parents
OR
Father
OR
Mother
OR
Carer
OR
Guardian
|
AND
|
Long-Term Hospitalisation
OR
Medical Intervention
OR
Rest
OR
Exercise
|
AND
|
Experience
OR
Perception
OR
Observation
OR
Understanding
OR
Judgement
|
It is crucial to determine Boolean operators within the PICO framework as it helps to effectively narrow down the research and make it more effective for researcher to gain a better understanding.
Databases
Databases used for researches provide effective insight to researcher to better perform the activity with utmost professionalism and ease, gathering only those information which is relevant and necessary for the research. Â For the same, EBSCO host platform has been utilised to determine databases which could help in conducting effective and timely research (Calvert, 2015). CINAHL and Mediline were the two databases that have been taken into consideration to gain an insight about the experience of parents whose children suffer from long-term hospitalisation. Both of these databases have ample amount of medical journals which provide relevant and effective information on various resources. With such abundance of medical literature present in these databases, it becomes quite efficient to gather relevant information regarding the research. The most contributing aspect of these databases is that information are timely updated for users to find the most recent and reliable information regarding their research topic.
Additional Search Strategies
Another type of strategy which has been used in this dissertation is Phrase Searching. It is a quite effective strategy where researcher could search their relevant research topics by using two or more words as phrases. This method is very crucial in case something specific has to be researched.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Within every research, it is of vital importance that only those information be included which is reliable, relevant and authenticated. A very strong reason for choosing such type of information is that it helps in keeping a narrow focus and the research does not deviate from its objectives. Thus, it is necessary for every researcher to segregate criteria that are either to be included in the research or excluded from the research (Hadi and Closs, 2016). Doing so would further ease researcher's work of gathering relevant information. These criteria for the research is mentioned below:
|
INCLUSION
|
EXCLUSION
|
RATIONALE
|
|
Research emphasised upon long-term hospitalisation of children
|
Research focused upon long-term hospitalisation of adults.
|
It would ensure that only information related to hospitalisation of children are taken into consideration.
|
|
Published between 2010 to 2017
|
Published before 2010.
|
Information beyond 2010 is more recent and relevant as per the requirements of research.
|
|
Qualitative Information
|
Quantitative Information
|
Since the research is about experience of parents whose children have been long-term hospitalised, qualitative research would result better in covering a broad subjective area.
|
|
Articles in English
|
Articles in other languages
|
It could be very hectic and tough for the researcher to translate the articles into English which would reduce the scope of effective information being gathered for the research.
|
Critical Evaluation
Critical Evaluation refers to a process which considers both positive and negative aspects of research in order to effectively bring out the best material and information forward which is essential for the research to be reliable, relevant and effective. It requires the researcher to be analytical and not mere descriptive. Being analytical needs all the strengths and weaknesses of research effectively evaluated for enhancing its understandability and applicability by completely removing those weaknesses. There are several critical appraisal tools available which could help the research to be utmost effective and rightfully applicable. It is crucial for researcher to choose the tool which increases scope of the research to be informative and helpful in nature. For the same, appraisal tool appropriate for this research is Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP), which would provide a framework for the researcher to enhance the quality of information and appraise all the relevant and reliable aspects of the overall data. This tool is very effective as it provides diversified methods to critically evaluate the research such as checklist for the researcher to conduct a systematic review of their research.
Method Of Analysis
Various methods and aspects are being used in this research to effectively fulfil each requirement. It is crucial to choose the most appropriate method of analysis in order to effectively carry out the research in a systematic manner. For the same, thematic analysis is being used to combine and align the findings for this dissertation. This is because it is an effective tool to derive a pattern and a flow from research findings (Braun and et. al., 2019). With a cluster of effective methods, this analysis is very flexible which further enhances its applicability. Within this analysis, inductive method is being utilised which would allow the researcher to develop contributing themes from the researched information in ways which could contribute in conduction of appropriate research.
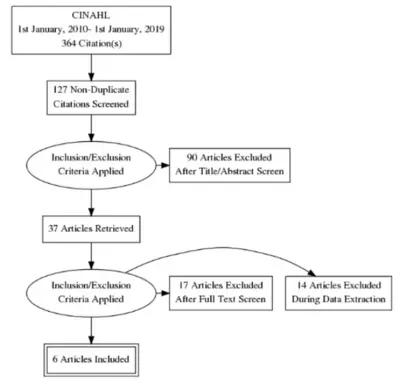
PRISMA Flow Chart
This flow chart clearly describes the stages through which information is gathered and analysed effectively. It describes each stage of collecting information from identification of crucial information to its induction. PRISMA flow chart enables researcher to describe the flow in which each article is read, screened and deemed eligible.
For this research, the PRISMA Flow Chart is described below:
CASP Checklist
Refer to Appendix- 1
Chapter 3- Findings
Within any research, it is quite imperative to determine the most relevant information that could satisfy the research aims and objective and helps in including the most appropriate type of information necessary to carry out the research as per the preset requirements (Noble and Smith, 2015). For experiences of parents during long-term hospitalisation of their children, more than 350 articles were screened throughout the information gathering process from which each article was rightfully screened, some of which were able to provide the most appropriate information. Ultimately, their eligibility was judged and only those articles are used which effectively provides information related to the research topic. Choosing appropriate information for the research effectively helped in performing in-depth analysis which could appropriately fulfil its agenda.
Study Characteristics
These characteristic enables appropriate and systematic segregation of the information gathered and methods used to collect them. It is an imperative practice which is crucial for the researcher to present relatable and relevant information which could be used to determine various aspects related to this research.
While most of the identified articles used qualitative methods like structured interview and synthesis, one article used numeric and quantitative approach to effectively give accurate and statistical information about the research study. It is crucial to conduct effective research which could satisfy research criteria and could be used systematically to use this for future studies.
Article Summary Table
|
Authors and Study Title
|
Date and Country
|
Objectives
|
Methods
|
Sample
|
Findings
|
Strengths and Limitations
|
|
Franck, L.S., and et. al., 2015. Predictors of parent post-traumatic stress symptoms after child hospitalization on general paediatric wards: a prospective cohort study. International journal of nursing studies. 52(1). pp.10-21.
|
2015,
San Francisco, United States; London, United Kingdom
|
The aim of this study was to identify the predictors or factors which induces post-traumatic stress symptoms followed after child hospitalisation
|
Standard questionnaires have been used to determine and identify the distress levels following hospitalisation of their children. In addition, correlation as well as multiple regression have been utilised to identify as to whether distress of parents and coping strategies as well as resources predicted PTS symptoms after 3 months of discharge of their children.
|
Parents whose children were admitted in paediatric ward were chosen as sample. 107 parents filled up questionnaires during hospitalisation as well as 3 months after their discharge.
|
Several parents were experiencing Post-Traumatic Stress Symptoms. While there were some too who elevated from any such symptoms. Moreover, various factors like self-blame, denial and other negative coping strategies along with uncertainty and anxiety were found as prominent factors which enhanced such symptoms.
|
While the study is effective enough to identify the predictors of post traumatic stress symptoms and their hospital experience. However, the study limits the methods through which further support could be given to the parents while hospitalisation of their children.
|
|
Wigert, H., Berg, M. and Hellström, A.L., 2010. Parental presence when their child is in neonatal intensive care. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences. 24(1). pp.139-146.
|
2010,
Sweden, Europe
|
The objective of this research was to determine factors which either facilitated or obstructed presence of parents while their child is present in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU).
|
Structured interview was undertaken by the researchers parents of two NICUs who registered specific timelines for which they were present in the hospital.
|
67 parents of 42 children were interviewed for this research where the interview was circled around their time spent in NICU and aspects affecting their presence.
|
Presence of parents at the NICU's were completely dependant upon the accommodation types offered. While occupants of parent rooms in at the units showed higher presence in comparison to those who stayed at maternity wards, homes or family hotels. The motivators of presence of parents were their responsibilities towards their children, condition of child and urge to have control. While a friendly environment, effective staff treatment and quality care served as facilitating factor, a non-friendly environment, parents' ill health and home responsibilities are the obstructing factors.
|
The study effectively reveals that there is a dire need for conditions of hospitals to be friendly which provides quite contributing and outstanding facilities to these parents and take their will of being with their children into consideration. However, the study limits the scope and ways which could ensure fulfilment of this need to facilitate presence of parents in such units.
|
|
Mikkelsen, G. and Frederiksen, K., 2011. Familyâ€ÂÂcentred care of children in hospital–a concept analysis. Journal of advanced nursing. 67(5). pp.1152-1162.
|
2011,
Denmark
|
This research aimed at conducting an effective analysis of provision of family-centred care to hospitalised children.
|
A systematic and appropriate literature review have been conducted including various articles and methodologies provided by Risjord to differentiate between colloquial and theoretical analysis and principles delivered by Penrod, Hupcey and Morse have been used to analyse concept's scientific maturity.
|
25 articles from 1951 to 2009 were utilised to conduct this analysis and to determine the concept of family-centred care given to hospitalised children.
|
This research weighed on the concept of developing healthy relationship between the management and parents which could provide a better care and treatment to hospitalised children. It also argued on the concept of involving parents at step of treatment to ensure a comfortable environment for them while their child is hospitalised.
|
While the arguments present in this research are strong enough to define the concept, it is still required of them to be clarified effectively to ensure better understanding of the research. It is still unclear on the partnership of professionals and parents and the conflict is not effectively explained in the research.
|
|
Kästel, A., Enskär, K. and Björk, O., 2011. Parents’ views on information in childhood cancer care. European Journal of Oncology Nursing. 15(4). pp.290-295.
|
2011,
Sweden
|
The aim of this research was to effectively identify the views of parents regarding information provided by the caring units whose children have been suffering from cancer.
|
Qualitative method have been chosen for the study. Structured interviews were conducted to derive information from families whose children have been suffering from cancer.
|
8 families, belonging to different backgrounds were indulged in five interviews each. The interviews of these personnels were taken during the initial year of illness of their child.
|
The results of these structured interview denoted the importance of fulfilling the needs of parents. Such fulfilment is purely based on the information which is provided to them. It also explored the manner and ease of procurement of information regarding the medical care. It determined the need for distinctive instructions to be given to parents to enhance their coping with the situations.
|
While the research carried out highlights ways in which improvement could be obtained through provision of information, however, the information limits to achieve aspects of provision of such information.
|
|
Ananth, P., and et. al., 2015. Hospital use in the last year of life for children with life-threatening complex chronic conditions. Pediatrics. 136(5). pp.938-946.Care Home
|
2015,
United States
|
The objectives of this research was to identify the hospital use by children who were suffering from Life-threatening Complex Chronic Conditions (LT-CCCs).
|
Quantitative Analysis is being used along with linear models to determine hospital days, admissions, costs as well as interventions like surgeries and mechanical ventilations.
|
1,252 children have been analysed in this research who were between the age group 1-18 years who, within 40 US hospitals, died in 2012. For such Quantitative analysis, Paediatric Health Information System database has been accessed to determine the statistical information derived for this study.
|
Quite useful information have been derived from this research which gave useful information about how many children required hospital services, costs incurred within their hospitalisation and diseases due to which long-term hospitalisation was required.
|
This research is quite useful to determine the type and number of conditions which require such intense medical attention and greatest hospital use. However, it lacks the qualitative aspects and experiences of parents and children who were hospitalised with such grieve diseases.
|
|
Smith, J., Swallow, V. and Coyne, I., 2015. Involving parents in managing their child's long-term condition—A concept synthesis of family-centered care and partnership-in-care. Journal of paediatric nursing. 30(1). pp.143-159.
|
2015,
United Kingdom
|
Objective of this research was to foster collaboration, engagement and empowerment as methods to effectively enhance the scope of improvement in treatments given to children suffering from long-term conditions.
|
Concept Synthesis has been used in the research to determine attributes and antecedents underpinning partnership in-care and family-centred care models.
|
For this qualitative research, 30 studies were effectively reviewed to determine factors which support the concept of this study.
|
Research finds all the factors which emphasise on entrenched professional practices, unclear roles as well as limited guidelines to support implementations. The central focus of this study was to identify ways in which trust could be built by professionals by taking their views into consideration. Â
|
The most effective aspect of this study is that it clearly provides a structure of how parent involvement could enhance the relationship between parents and professionals and how such effective partnerships could support the parents of children with long-term conditions.
|
Identification of Themes
After determining appropriate research articles, next step calls for identification of prominent themes which could further give an in-depth review of the study. For this research, most crucial themes are described below:
Theme 1: Impact of Long-term hospitalisation of children on parents' health
From this research, almost all the articles determined effectively the impact of long-term hospitalisation of children on the health of parents. Parents seem to be suffering from post traumatic stress symptoms even after discharge of their children. The article by Linda S. Franck, Jo Wray, Caryl Gay, Annette K. Dearmun, Kristy Lee and Bruce A. Cooper, (2015), effectively determines that there are various conditions which induces such a negative aspect and stress on parents while their child is hospitalised.
You Share Your Assignment Ideas
We write it for you!
Most Affordable Assignment Service
Any Subject, Any Format, Any Deadline
Order Now View Samples
Out of all the subjects, 32.7% of parents showed levels of post traumatic stress symptoms. This research also gives an insight to the need of various actions that are required to be taken to improve this experience and reduction of such a stress.
Theme 2: Factors influencing parental presence in hospital
The article by Helena Wigert, Marie Berg, Anna-Lena Hellstorm, (2010) gives a quite crucial theme for determining experience of parents while in hospital. This study effectively determines that there are various factors which influences parents' time in hospital, especially in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.
Interviews by various parents helped in a structured analysis of the factors that either obstruct or facilitate their presence with their children. The study derives that if the environment is friendly and supportive, parents are likely to be then involved while their children are present in the hospital. However, the opposite restrains and restricts their presence in the hospital. As per this research, it derives that effective and contributing environment is in dire need for hospitals to enhance the involvement of parents in medical processes of the unit. In addition to this, the theme also identifies that attention must be given to parents to consider whether they like to be present or not. It must be upon their own will to witness the treatment given to their children by the NICU.
More Suggested:Â
Theme 3: Family-centred care
As per the study by Gitte Mikkelsen and Kirsten Frederiksen, (2011), family-centred care is a concept that must be included in giving healthcare services to children. This study gives light to the concept that it would influence care given to hospitalised children by involving their parents in treatments.
However, this aspect has its own advantages and limitations and such consequences are outlined as well as discussed within this study. It also outlines the perspective of ill children and analysis the intensity in which the involvement of parents should be within the treatment. Thus, this theme has put emphasis on the concept of family-centred care and its application within healthcare settings.
Theme 4: View of parents on information provided to them
From information presented above in the article by Anne Kästel, Karin Enskär and Olle Björk, (2011), parents must be given importance while disclosing crucial information about harmful medical conditions like cancer. This study makes way for how improvement could be achieved in treatment as well as how parents could better cope up with their child's illness. However, while approaching parents regarding their views on information provided to them, dissimilar and contrast views were given in respect to acquisition of information. While the study reveals that some parents acquired necessary information quite easily, others really had to struggle for it. This theme provides a deep insight on how, when and what information must be provided to parents which hospitalised children. It gives a light on current practice and how improvements could be achieved in respect to provision of information and dealing with hospitalisation of children.
Theme 5: Hospital use of children
A study by Prasanna Ananth, Patrice Melvin, Chris Feudtner, Joanne Wolfe and Jay G. Berry, (2015), highlights aspects regarding hospital usage of children suffering from Life-Threatening Complex Chronic Conditions. This quantitative approach gives insight to various conditions which causes long-term hospitalisation and frequent hospital use of children.
This study has used quantitative methods like use of statistics and effective data applying a range of multi-variable analysis taking information of numerous hospitals into consideration. Through such a wide analysis, research reveals that various diseases and life-threatening conditions results in such robust and intensive requirements for hospital and medical services.
 The research reveals that cost incurred by parents to acquire medical services depends heavily on condition their child is suffering with. It revealed that children suffering from immunological/haematological conditions required greatest hospital used along with various other conditions including respiratory systems, metabolism, etc. Thus, this theme would be useful regarding information about a number of chronic conditions inducing higher hospital use and cost incurred for the same. However, still this research is purely based on statistical and quantitative information and lacks in providing a qualitative insight on experiences of parents of children suffering from such conditions.
Theme 6: Achievement of improvement in treatments
Joanna Smith, Veronica Swallow and Imelda Coyne, (2015) through their article, provided their a combined view of how involving parents of children suffering with long-term conditions could help in achieving improvement in nursing and medical practices. Parents, in this study are given central role considering their knowledge about their children and prioritising their concern while treating their child to ensure a better health condition. This theme emphasise the need to improve collaboration of medical professionals and parents ensuring quality treatment given to children suffering with long-term conditions. Existing practices along with their limitations are evaluated by this theme in hope to improve experience of parents whose children are hospitalised.
Summary
This chapter is quite effective in emphasising on parents' experiences while their child is hospitalised for long-term. It gives a detailed and critical review of the literature and showed areas and aspects covered by the articles in respect to determining experiences of parents. This chapter also identifies the need for further recommendations in existing medical practice that could ensure effective improvements in parents' conditions and experiences while their children are hospitalised.
Chapter 4- Discussion
This chapter undertakes a brief discussion of themes mentioned above in respect to existing medical guidelines and literature. All the six themes identified above provides analysis and useful information about parents' experiences. However, below is the discussion of various themes used in this research which emphasises on experiences of parents:
Discussion on Themes
Parental Health
The existing literature is based on impact on parents' health while their children remain hospitalised. It is quite a negative experience which makes it natural to implicate negative impact on their health. Non-cooperation and non-acquisition of support and effective information about their children' s health amplifies the negative effects on their health. This also cause difficulties in treatments given to their children.
As per Frank Muscara and et. al. (2015), the experience of parents having children with some serious illness is quite distressing. The degree up to which distress levels affects these parents and their coping up with such levels depends on different individuals. While some shows spontaneous recovery, others take a substantial amount of time. The existing literature presents information about various symptoms and after effects like Post -Traumatic Stress Symptoms which negatively impacts their health to sometimes clinically dangerous methods. This study calls for support given to such parents and take measures to understand their condition and provide them with utmost support and comfort to better cope up with the situation.
Parental Presence
As per various guidelines set out by General Medical Council UK, parents must be considered while providing treatment to their children. Their presence must be dependant on their own will while treatment is given to their child. However, it is crucial that the professionals provide them effective and friendly environment for them to be present and provide their assistance in care given to their child. Â Such support would put a positive impact on their experience and it could help in building an effective bond and sense of optimism in their minds. Such positive thinking could allow them to cope up with situation and illness of their child in a better manner and would be better for their health.
Family-centred care
Within medical and healthcare settings, a need which is constantly arising is the adoption of a culture fostering family-centred care given in hospitals. It is a practice of developing an effective relationship between parents and the medical professionals. However, current practices are not very much inclined in ways which promotes this practice. According to a research by Shields, L., and et. al., (2012), this practice must be included in healthcare settings in a way which could ensure quality treatment. This theme puts emphasis on ensuring satisfaction of parents.
However, there are negative implications of this practice. As per guidelines by General Medical Council, UK, patient must be a doctor's first concern. While their hospitalisation, there are various harsh measures and treatments that are required to be taken to ensure safety of the patient. Involvement of parents and providing family-centred care might reduce or in some cases, eradicate the possibility for professionals to take such measures. It is thus, necessary for these professionals to include parents of children who are hospitalised but must govern their decisions which is in the best interest of patients.
Parents' view on information
Appropriate, timely and accurate information is necessary to ensure quality care. It consists of treatment provided to their child, medicines regarding their treatment, possible after effects, etc. Such aspects provide information to parents about whether appropriate treatment is being given to their child or not. As per Department of Health, parents possess the right to access each and every information which concerns healthcare provided to their child.
This research depicts that consent plays a very important role in giving accurate and effective treatment to children. However, current practice within the healthcare is required to improve this element to elevate the experience parents have while hospitalisation of their children. Providing all the possible information timely would enable parents to cope better with serious illnesses like cancer. Thus, it is of vital importance that the right to information is accessed by parents and is well provided by professionals.
Hospital Usage
This theme its centred around children's hospital use. Information of such aspect is quite useful in terms of determining type of diseases and illness which causes long-term hospitalisation of children. Such studies give insight as to what medical prevention measures must be taken to reduce such vast numbers of hospital usage. While the existing literature emphasises on rising hospital admissions, National Health Service, has drawn out various guidelines which could be implemented by parents and carers to ensure protection of their children from various harmful diseases and chronic conditions.
According to these guidelines, people must take various measures to protect children from suffering chronic diseases and other severe illness. These guidelines include various hygienic methods and other measures that could be taken in order to ensure less hospital use and admissions. Â
Improvement in Treatments
Existing literature emphasised on demand of improving the medical practices and treatments provided by professionals to children with long-term conditions. The main aspect of this theme relates with involving parents during healthcare services.
Antje Aarthun, Knut A. Øymar and Kristin Akerjordet, (2019) gave insight on how decision-making while provision of care could improve due to parental involvement during hospitalisation of children. According to their study, parents' experience and their ability to deal with their child' s situation could enhance if their role is increased in healthcare provided to their offspring. Medical professional and healthcare staff have a very prominent role in strengthening parents' sense of consistency and cooperation which could enhance scope of quality care and could help achieving improvement in experience of parents whose children have been hospitalised.
Recommendations for research, practice and education
There is always a scope of improvement in every research and effective guidance would further provide room for recommendation which could remove and reduce the limitations of literature review. There are three wide areas where these recommendations could be applied:
Research
Various studies undertaken to determine parents' experience during long-term hospitalisation of their children requires a broader scope and wider research to cover the areas of limitations as well. For instance, study by Prasanna Ananth, Patrice Melvin, Chris Feudtner, Joanne Wolfe and Jay G. Berry, (2015) could have researched on various qualitative aspects regarding experiences of parents bearing the loss of children with chronic conditions. Along with this, Helena Wigert, Marie Berg, Anna-Lena Hellstorm, (2010) could have further developed their study to define methods through which parental presence could have been facilitated.
Practice
The whole study and each article depicted that an immediate need is arising to ensure that modifications in existing healthcare practice are required to be implemented. The sole reason being welfare of patients as well as experiences of parents. Healthcare staff must play a vital role in determining that effective information is being provided to parents along with proper support and comfort given to parents whose children are within the premises requiring medical attention. Such practices would enhance professionalism along with ensuring trust between the hospital management and parents.
Education
It is a dire need to educate healthcare professionals the methods that could be applied to amplify a sense of comfort and trust in parents and allow them to give their full support and consent to measures and treatment methods applied by hospitals. Moreover, parents of hospitalised children must also be educated in terms of dealing in a better manner with child's illness and methods which could be applied by them to ensure that their child gets proper care even after their discharge from the healthcare facilities.
Review Limitations
Outlining limitations gives scope for further improvement and ensuring better practice in ways which could contribute to a better research. The study conducted above was based on a topic that was quite subjective in nature. Thus, it was a very hectic task to gather information that could seem accurate and serve well to research criteria. Various resources have been utilised to fulfil the requirements of this study, such as time and cost. Limited resources were applicable to conduct a research with such vast scope and area of coverage and thus, it was difficult for including each aspect of such a study. Along with this, with such a subjective content, each perspective has to be taken into consideration which serve effectively to the research which requires expertise and enhanced knowledge. However, maximum effort and attempt have been put in to conduct the study and include each aspect contributing to fulfilment of its agenda and analysing parents' experience effectively.
Conclusion
Thus, it is concluded from the above information, that it is crucial to determine parents' experiences whose children have been long-term hospitalised. Various research methods like thematic analysis could be utilised to conduct effective research and collect information that could be used to analyse aspects of the research. Lastly, it is crucial to improve medical practices and training and education must be given to health care professionals in order to achieve improvement in experiences of parents of long-term hospitalised children.
References
- Aarthun, A., Øymar, K.A. and Akerjordet, K., 2019. Parental involvement in decisionâ€ÂÂmaking about their child’s health care at the hospital. Nursing open. 6(1). pp.50-58.
- Ananth, P., and et. al., 2015. Hospital use in the last year of life for children with life-threatening complex chronic conditions. Pediatrics. 136(5). pp.938-946.
- Braun, V., and et. al., 2019. Thematic analysis. Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences, pp.843-860.
- Calvert, K., 2015. Maximizing academic library collections: measuring changes in use patterns owing to EBSCO Discovery Service. College & Research Libraries. 76(1). pp.81-99.
- Franck, L.S., and et. al., 2015. Predictors of parent post-traumatic stress symptoms after child hospitalization on general paediatric wards: a prospective cohort study. International journal of nursing studies. 52(1). pp.10-21.
- Hadi, M.A. and Closs, S.J., 2016. Ensuring rigour and trustworthiness of qualitative research in clinical pharmacy. International journal of clinical pharmacy. 38(3). pp.641-646.
- Kästel, A., Enskär, K. and Björk, O., 2011. Parents’ views on information in childhood cancer care. European Journal of Oncology Nursing. 15(4). pp.290-295.
- Mikkelsen, G. and Frederiksen, K., 2011. Familyâ€ÂÂcentred care of children in hospital–a concept analysis. Journal of advanced nursing. 67(5). pp.1152-1162.
Amazing Discount
UPTO55% OFF
Subscribe now for More
Exciting Offers + Freebies